|
Vala Sciences圖像細胞計數(shù)儀
經(jīng)過幾十年的不斷研究��、開發(fā)和市場表現(xiàn)��,圖像細胞計數(shù)儀憑借其標準高速和高質(zhì)量圖像����,成為在高內(nèi)涵篩選的行業(yè)標準。利用大功率固態(tài)照明��,基于圖像的超速自動對焦和*新科技相機����,圖像細胞計數(shù)儀為大規(guī)模的成像應(yīng)用中*具挑戰(zhàn)性的篩選量需求�,提供了解決方案。
圖像細胞計數(shù)儀的特點:
靈敏度
超高質(zhì)量圖像的獲得基于*初簡單而優(yōu)雅的光學(xué)布局����。我們的光學(xué)設(shè)計師在大腦中勾勒出圖像細胞計數(shù)儀系統(tǒng)簡單的光學(xué)系統(tǒng),*大化的減少光學(xué)組件����,保證*好的光學(xué)質(zhì)量���。產(chǎn)生的圖像信噪比*小。光效率的提高�,明亮的固態(tài)照明和高度敏感的相機大大地減少了曝光時間,提高了掃描速度���。
對焦
圖像細胞計數(shù)儀的成像原理的核心即是要獲取*佳聚焦����。結(jié)合多項**技術(shù)以及多年的**改進�,Vala基于圖像的自動對焦,輔以激光表面跟蹤���,在不降低掃描速度的情況下��,確保其在每個領(lǐng)域獲得*好的對焦����。
靈活
圖像細胞計數(shù)儀具備很大的靈活性���。儀器支持大量的成像孔板�����,輸出非**的TIFF格式圖像��,可以用于任何后續(xù)軟件的分析����。還支持其他專業(yè)文件格式可選的輸出。大量的激發(fā)光源和發(fā)射光濾過可使任何熒光團在圖像細胞計數(shù)儀中可見���。圖像細胞計數(shù)儀支持各種倍數(shù)的放大����,包括4x�, 10x, 20x 和40x�。
集成和占地面積
占地空間小、無縫機械和軟件集成使其成為一種優(yōu)良的適合獨立和自動化應(yīng)用程序的儀器�,Vala還提供了各種各樣的機器人提出完全自動化的解決方案���。
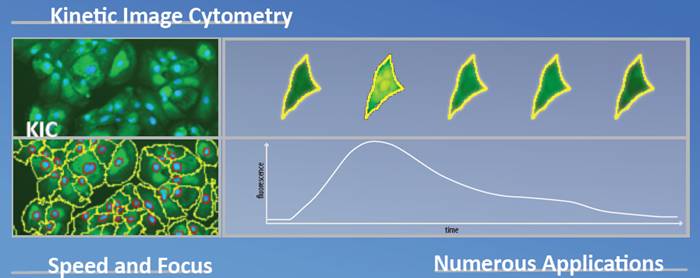
Vala Sciences Kinetic圖像細胞儀 (KIC) 可以利用自動高通量方法對每個孔板中的成百上千個細胞進行單個細胞鈣離子瞬時流動進行分析���,從成千上萬個化合物中快速篩選出用于心律失常的活性化合物。而且,KIC通過整合的細胞刺激信號�����,可以對具有自律性的心肌細胞或電同步細胞進行錄像�����。
Vala Sciences品牌 IC200-KIC高內(nèi)涵篩查系統(tǒng)

Vala Sciences IC200-KIC?是一個功能齊全的高內(nèi)涵篩查系統(tǒng)��,也能夠捕獲高速時間序列圖像�����。IC200使用基于圖像的自動對焦和激光表面跟蹤��,確保每一個圖像在*佳焦點聚焦�。擁有很多物鏡和孔板支持以及占用空間小的特點,IC200的功能是***的����。靈活的模塊化設(shè)計使得這個系統(tǒng)成為一個很好的定制解決方案的平臺。
特點:

1.完整的高通量篩選方案
2.超靈敏5.53MP SCMOS相機
3.動力學(xué)細胞圖像分析
3.1)0.1-100fps圖像采集和分析
4. 全自動刺激方案
4.1)電場
4.2)光遺傳學(xué)
4.2)液體處理
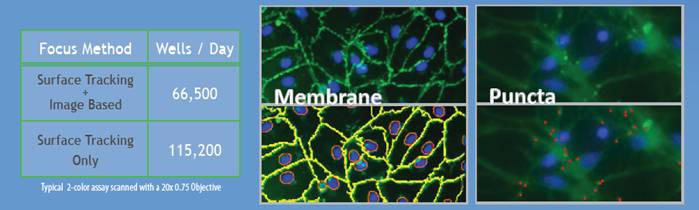
5.合式自動對焦:表面跟蹤+圖像基于
6.可用機器人自動化解決方案
7.可用的企業(yè)數(shù)據(jù)存儲解決方案
8.Benchtpop Footprint: 21" x 21 " x 24.5" (W×D×H×)
技術(shù)參數(shù)
照相機
|
兩個553萬像素的CMOS 相機
|
|
物鏡
|
平場復(fù)消色差物鏡 4x NA 0.20 (1.63 um/Pixel)
平場復(fù)消色差物鏡10x NA 0.45 (0.64 um/Pixel)
平場復(fù)消色差物鏡 20X NA 0.75 (0.32 um/Pixel)
平場復(fù)消色差物鏡 40X NA 0.95 (0.16 um/Pixel)
平場復(fù)消色差物鏡 60X NA 0.95 (0.11 um/Pixel)
|
|
自動對焦
|
表面跟蹤和圖像對焦
- 容錯(無誤差)在每個視野內(nèi)準確對焦
- 在每個視野內(nèi)執(zhí)行< 0.5秒的自動對焦
|
|
物鏡定位器
|
專業(yè)的超快的100納米分辨率的定位器
|
|
階段
|
100納米分辨率XY編碼階段����。
|
|
孔板支持
|
支持1536, 384,96�, 48,24�����,12 和 6 孔板
能夠定義自定義格式
|
|
激發(fā)光源
|
固態(tài)光引擎7 UV-Vis-IR�,可運行 15000多個小時
|
|
發(fā)射濾光輪
|
10個方位的發(fā)射濾光輪
|
|
標準濾光片組
|
- DAPI,F(xiàn)ITC�����,TRITC����,Cy5 and Cy7標準
- 其他濾光片組
|
|
大小
|
21" x 21" x 22" (53cm x 53cm x 56cm)外形尺寸包括光引擎
|
|
動態(tài)圖像血細胞計數(shù)儀(KIC?)
|
|
采樣頻率
|
以0.1-100幀/秒的頻率采集時間序列
- 延時采集圖像的重復(fù)序列
|
|
刺激的選擇
|
- 電刺激:自動選擇電*.
- 光遺傳學(xué): 光刺激可利用一切激發(fā)光源.
- 添加化合物:可選液體處理選項.
|
|
選擇
|
|
同步采集
|
雙攝像頭選項用于同時捕獲兩個通道
|
|
環(huán)境控制
|
溫度 (30-40° C) and CO2 (5-10%)
- 低氧(5%,10% 或15%)
|
|
機械自動化
|
完整的機器人處理包
|
|
集成
|
可用API集成到現(xiàn)有的平臺
|
圖像細胞計數(shù)儀310(IC310)
—速度*快高內(nèi)涵篩選系統(tǒng)

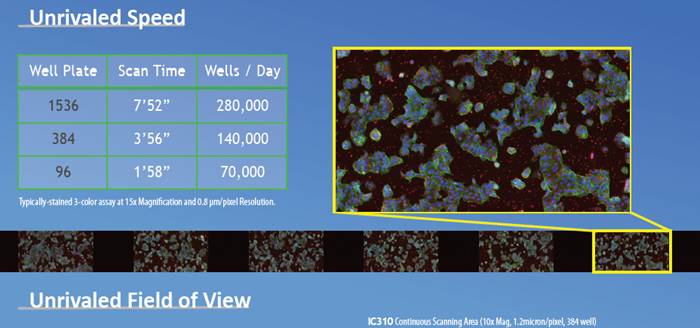
Vala Sciences IC310是目前市場上執(zhí)行速度*快的高內(nèi)涵篩選系統(tǒng)�����。它通過對圖像形態(tài)的一個連續(xù)掃描��,捕捉移動圖像��。樣品不是停留在每個孔板中被捕獲到圖像�,因此節(jié)約了時間。消除了每個孔板中進行減速�、停止和加速的耗時,使該系統(tǒng)掃描速度*快�����,每1536板花費不到8分鐘的時間即可完成全過程�����。因為1536個孔板一直處于被捕捉的狀態(tài)�,IC310允許用戶自行選擇多少個字段保存到磁盤,不需要考慮掃描速度���。
特點
1.超高通量
Ultra high throughput
-up to 280000 wells per day on a typically field of view
2.User Throughput Trade-Off for large FOV scanning
3.Up to 0.8um/pixel Resolution at 15 x 0.45NA
4.Multi Camera Options Available
5.Robotic Automation Solutions Available
6.Enterprise Date Storage Solutions Available
7.Benchtpop Footprint: 21" x 21 " x 24.5" (W×D×H×)

|
照相機
|
3個高度靈敏的TDI相機以10倍的放大倍數(shù)掃描���,每次掃描覆蓋全部的1536個孔板
|
|
物鏡
|
-平場復(fù)消色差物鏡4x NA 0.2 (3.0 um/Pixel 標準或2.0 um/Pixel with 1.5x Relay Option)
-平場復(fù)消色差物鏡10x NA 0.45 (1.2 um/Pixel 標準或 0.8 um/Pixel with 1.5x Relay Option)
|
|
自動對焦
|
激光表面發(fā)射追蹤
|
|
物鏡定位器
|
專業(yè)的超快的100納米分辨率的定位器
|
|
階段
|
100納米分辨率XY編碼階段。
|
|
孔板支持
|
支持1536�����, 384��,96���, 48��,24��,12 和 6 孔板
|
|
激發(fā)光源
|
激光引擎2線標準
-可升級到5線標準
|
|
發(fā)射濾光輪
|
10個方位的發(fā)射濾光輪
|
|
標準濾光片組
|
- DAPI���,F(xiàn)ITC���,TRITC,Cy5 and Cy7標準
- 其他濾光片組
|
|
大小
|
21" x 21" x 22" (53cm x 53cm x 56cm)外形尺寸包括光引擎
|
|
選擇
|
|
同步采集
|
三個攝像頭選項用于同時捕獲三個通道
|
|
環(huán)境控制
|
溫度 (30-40° C) and CO2 (5-10%)
- 低氧(5%�����,10% 或15%)
|
|
機械自動化
|
完整的機器人處理包
|
|
集成
|
可用API集成到現(xiàn)有的平臺
|
valasciences服務(wù)& 產(chǎn)品—高內(nèi)涵篩選服務(wù)

作為一個EPA認證的 ToxCAST篩查項目的分包商和分析提供者�,我們*近被賦予一個“特殊”提供評級的服務(wù)。
我們的服務(wù)包括100多種原代細胞和干細胞有關(guān)的高內(nèi)涵篩選分析項目���,很多可以對項目進行改編或定制的回答特定的生物學(xué)問題�����。
我們專注于使用動態(tài)圖像血細胞計數(shù)器(KIC)平臺的高通量心臟毒性篩選合作開發(fā)分析和數(shù)據(jù)分析方法��。
使用**的模型包括ips來源的細胞專門從事定制分析
專注于高質(zhì)量的數(shù)據(jù)和生物相關(guān)性
Publications:
I. Kinetic Image Cytometry:
1.
Wahlquist, C., Jeong, D., Rojas-Munoz, A., Kho, C., Lee,
A., Mitsuyama, S., van Mil, A., Park, W.J., Sluijter, J.P., Doevendans, P.A.,
Hajjar, R.J. & Mercola, M. Inhibition of miR-25 improves cardiac
contractility in the failing heart. Nature 508, 531-535 (2014).
2.
Cerignoli, F., Charlot, D., Whittaker, R., Ingermanson,
R., Gehalot, P., Savchenko, A., Gallacher, D.J., Towart, R., Price, J.H., McDonough,
P.M. & Mercola, M. High throughput measurement of Ca2+ dynamics for
drug risk assessment in human stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes by kinetic image
cytometry. J Pharmacol Toxicol Methods 66, 246-256 (2012).
3.
Islas, J.F., Liu, Y., Weng, K.C., Robertson, M.J., Zhang,
S., Prejusa, A., Harger, J., Tikhomirova, D., Chopra, M., Iyer, D., Mercola,
M., Oshima, R.G., Willerson, J.T., Potaman, V.N. & Schwartz, R.J.
Transcription factors ETS2 and MESP1 transdifferentiate human dermal
fibroblasts into cardiac progenitors. Proceedings of the National Academy of
Sciences of the United States of America 109, 13016-13021 (2012).
4.
Charlot, D., Campa, V., Azimi, B., Mercola, M.,
Ingermanson, R., McDonough, P.M. & Price, J.H. Automated calcium
measurements in live cardiomyocytes. in 5th IEEE International Symposium on
Biomedical Imaging: From Nano to Macro, Link. 316-319 (2008).
II. IC100 and IC200:
5.
Bharadwaj, U., Eckols, T.K., Kolosov, M., Kasembeli,
M.M., Adam, A., Torres, D., Zhang, X., Dobrolecki, L.E., Wei, W., Lewis, M.T.,
Dave, B., Chang, J.C., Landis, M.D., Creighton, C.J., Mancini, M.A. &
Tweardy, D.J. Drug-repositioning screening identified piperlongumine as a
direct STAT3 inhibitor with potent activity against breast cancer. Oncogene
0(2014).
6.
Bolt, M.J., Stossi, F., Callison, A.M., Mancini, M.G.,
Dandekar, R. & Mancini, M.A. Systems level-based RNAi screening by high
content analysis identifies UBR5 as a regulator of estrogen receptor-alpha
protein levels and activity. Oncogene (2014).
7.
Chung, T.D. Collaborative pre-competitive preclinical
drug discovery with academics and pharma/biotech partners at Sanford|Burnham:
infrastructure, capabilities & operational models. Combinatorial chemistry
& high throughput screening 17, 272-289 (2014).
8.
Stossi, F., Bolt, M.J., Ashcroft, F.J., Lamerdin, J.E.,
Melnick, J.S., Powell, R.T., Dandekar, R.D., Mancini, M.G., Walker, C.L.,
Westwick, J.K. & Mancini, M.A. Defining estrogenic mechanisms of bisphenol
A analogs through high throughput microscopy-based contextual assays. Chemistry
& biology 21, 743-753 (2014).
9.
Large, M.J., Wetendorf, M., Lanz, R.B., Hartig, S.M.,
Creighton, C.J., Mancini, M.A., Kovanci, E., Lee, K.F., Threadgill, D.W.,
Lydon, J.P., Jeong, J.W. & DeMayo, F.J. The epidermal growth factor
receptor critically regulates endometrial function during early pregnancy. PLoS
genetics 10, e1004451 (2014).
10. Bolt, M.J.,
Stossi, F., Newberg, J.Y., Orjalo, A., Johansson, H.E. & Mancini, M.A.
Coactivators enable glucocorticoid receptor recruitment to fine-tune estrogen
receptor transcriptional responses. Nucleic acids research 41, 4036-4048
(2013).
11. Castro, D.J.,
Maurer, J., Hebbard, L. & Oshima, R.G. ROCK1 inhibition promotes the self-renewal
of a novel mouse mammary cancer stem cell. Stem cells 31, 12-22 (2013).
12. Kostrominova,
T.Y., Reiner, D.S., Haas, R.H., Ingermanson, R. & McDonough, P.M. Automated
methods for the analysis of skeletal muscle fiber size and metabolic type.
International review of cell and molecular biology 306, 275-332 (2013).
13. McDonough, P.M.,
Maciejewski-Lenoir, D., Hartig, S.M., Hanna, R.A., Whittaker, R., Heisel, A.,
Nicoll, J.B., Buehrer, B.M., Christensen, K., Mancini, M.G., Mancini, M.A.,
Edwards, D.P. & Price, J.H. Differential phosphorylation of perilipin 1A at
the initiation of lipolysis revealed by novel monoclonal antibodies and high
content analysis. PloS one 8, e55511 (2013).
14. Prigozhina,
N.L., Heisel, A.J., Seldeen, J.R., Cosford, N.D. & Price, J.H. Amphiphilic
suramin dissolves Matrigel, causing an 'inhibition' artefact within in vitro
angiogenesis assays. International journal of experimental pathology 94,
412-417 (2013).
15. Dasgupta, I.,
Tanifum, E.A., Srivastava, M., Phatak, S.S., Cavasotto, C.N., Analoui, M. &
Annapragada, A. Non inflammatory boronate based glucose-responsive insulin
delivery systems. PloS one 7, e29585 (2012).
16. Ding, Z.,
German, P., Bai, S., Feng, Z., Gao, M., Si, W., Sobieski, M.M., Stephan, C.C.,
Mills, G.B. & Jonasch, E. Agents that stabilize mutated von Hippel-Lindau
(VHL) protein: results of a high-throughput screen to identify compounds that
modulate VHL proteostasis. Journal of biomolecular screening 17, 572-580
(2012).
17. Hartig, S.M.,
He, B., Newberg, J.Y., Ochsner, S.A., Loose, D.S., Lanz, R.B., McKenna, N.J.,
Buehrer, B.M., McGuire, S.E., Marcelli, M. & Mancini, M.A. Feed-forward
inhibition of androgen receptor activity by glucocorticoid action in human
adipocytes. Chemistry & biology 19, 1126-1141 (2012).
18. Slattery, S.D.,
Newberg, J.Y., Szafran, A.T., Hall, R.M., Brinkley, B.R. & Mancini, M.A. A
framework for image-based classification of mitotic cells in asynchronous
populations. Assay and drug development technologies 10, 161-178 (2012).
19. Uray, I.P.,
Rodenberg, J.M., Bissonnette, R.P., Brown, P.H. & Mancini, M.A.
Cancer-preventive rexinoid modulates neutral lipid contents of mammary
epithelial cells through a peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor
gamma-dependent mechanism. Molecular pharmacology 81, 228-238 (2012).
20. Zhang, X., Bolt,
M., Guertin, M.J., Chen, W., Zhang, S., Cherrington, B.D., Slade, D.J.,
Dreyton, C.J., Subramanian, V., Bicker, K.L., Thompson, P.R., Mancini, M.A.,
Lis, J.T. & Coonrod, S.A. Peptidylarginine deiminase 2-catalyzed histone H3
arginine 26 citrullination facilitates estrogen receptor alpha target gene
activation. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United
States of America 109, 13331-13336 (2012).
21. Ashcroft, F.J.,
Newberg, J.Y., Jones, E.D., Mikic, I. & Mancini, M. High content imaging-based
assay to classify estrogen receptor-alpha ligands based on defined mechanistic
outcomes. Gene (2011).
22. Hartig, S.M.,
He, B., Long, W., Buehrer, B.M. & Mancini, M.A. Homeostatic levels of SRC-2
and SRC-3 promote early human adipogenesis. J Cell Biol 192, 55-67 (2011).
23. Prigozhina,
N.L., Heisel, A., Wei, K., Noberini, R., Hunter, E.A., Calzolari, D., Seldeen,
J.R., Pasquale, E.B., Ruiz-Lozano, P., Mercola, M. & Price, J.H.
Characterization of a novel angiogenic model based on stable, fluorescently
labelled endothelial cell lines amenable to scale-up for high content
screening. Biol Cell 103, 467-481 (2011).
24. Quintavalle, M.,
Elia, L., Price, J.H., Heynen-Genel, S. & Courtneidge, S.A. A cell-based
high-content screening assay reveals activators and inhibitors of cancer cell
invasion. Science signaling 4, ra49 (2011).
25. Yip, K.W.,
Cuddy, M., Pinilla, C., Giulanotti, M., Heynen-Genel, S., Matsuzawa, S. &
Reed, J.C. A high-content screening (HCS) assay for the identification of
chemical inducers of PML oncogenic domains (PODs). Journal of biomolecular
screening 16, 251-258 (2011).
26. Garcia-Becerra,
R., Berno, V., Ordaz-Rosado, D., Sharp, Z.D., Cooney, A.J., Mancini, M.A. &
Larrea, F. Ligand-induced large-scale chromatin dynamics as a biosensor for the
detection of estrogen receptor subtype selective ligands. Gene 458, 37-44
(2010).
27. Kiselyuk, A.,
Farber-Katz, S., Cohen, T., Lee, S.H., Geron, I., Azimi, B., Heynen-Genel, S.,
Singer, O., Price, J., Mercola, M., Itkin-Ansari, P. & Levine, F.
Phenothiazine neuroleptics signal to the human insulin promoter as revealed by
a novel high-throughput screen. Journal of biomolecular screening 15, 663-670
(2010).
28. McDonough, P.M.,
Ingermanson, R.S., Loy, P.A., Koon, E.D., Whittaker, R., Laris, C.A., Hilton,
J.M., Nicoll, J.B., Buehrer, B.M. & Price, J.H. Quantification of Hormone
Sensitive Lipase Phosphorylation and Colocalization with Lipid Droplets in
Murine 3T3L1 and Human Subcutaneous Adipocytes via Automated Digital Microscopy
and High-Content Analysis. Assay and drug development technologies (2010).
29. Narayanan, R.,
Yepuru, M., Szafran, A.T., Szwarc, M., Bohl, C.E., Young, N.L., Miller, D.D.,
Mancini, M.A. & Dalton, J.T. Discovery and mechanistic characterization of
a novel selective nuclear androgen receptor exporter for the treatment of
prostate cancer. Cancer Res 70, 842-851 (2010).
30. Whittaker, R.,
Loy, P.A., Sisman, E., Suyama, E., Aza-Blanc, P., Ingermanson, R.S., Price,
J.H. & McDonough, P.M. Identification of MicroRNAs that control lipid
droplet formation and growth in hepatocytes via high-content screening. Journal
of biomolecular screening 15, 798-805 (2010).
31. Zou, J., Ganji,
S., Pass, I., Ardecky, R., Peddibhotla, M., Loribelle, M., Heynen-Genel, S.,
Sauer, M., Pass, I., Vasile, S., Suyama, E., Malany, S., Mangravita-Novo, A.,
Vicchiarelli, M., McAnally, D., Cheltsov, A., Derek, S., Shi, S., Su, Y., Zeng,
F.Y., Pinkerton, A.B., Smith, L.H., Kim, S., Ngyuen, H., Zeng, F.Y., Diwan, J.,
Heisel, A.J., Coleman, R., McDonough, P.M. & Chung, T.D.Y. Potent
inhibitors of lipid droplet formation. in Probe Reports from the NIH Molecular
Libraries Program (Bethesda (MD), 2010).
32. Buck, T.E., Rao,
A., Coelho, L.P., Fuhrman, M.H., Jarvik, J.W., Berget, P.B. & Murphy, R.F.
Cell cycle dependence of protein subcellular location inferred from static,
asynchronous images. Conf Proc IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc 2009, 1016-1019 (2009).
33. Coelho, L.P.,
Shariff, A. & Murphy, R.F. Nuclear Segmentation in Microscope Cell Images:
A Hand-Segmented Dataset and Comparison of Algorithms. Proc IEEE Int Symp
Biomed Imaging 5193098, 518-521 (2009).
34. Giordano, C.,
Cui, Y., Barone, I., Ando, S., Mancini, M.A., Berno, V. & Fuqua, S.A.
Growth factor-induced resistance to tamoxifen is associated with a mutation of
estrogen receptor alpha and its phosphorylation at serine 305. Breast Cancer
Res Treat 119, 71-85 (2009).
35. Heynen-Genel, S.
& Price, J. Cytometric Features of Fluorescently Labeled Nuclei for Cell
Classification. in Handbook of Medical Image Processing and Analysis, Vol. 1
(ed. Bankman, I.) 453-463 (Academic Press, 2009).
36. McDonough, P.M.,
Agustin, R.M., Ingermanson, R.S., Loy, P.A., Buehrer, B.M., Nicoll, J.B.,
Prigozhina, N.L., Mikic, I. & Price, J.H. Quantification of Lipid Droplets
and Associated Proteins in Cellular Models of Obesity via
High-Content/High-Throughput Microscopy and Automated Image Analysis. Assay and
drug development technologies (2009).
37. Slattery, S.D.,
Mancini, M.A., Brinkley, B.R. & Hall, R.M. Aurora-C kinase supports mitotic
progression in the absence of Aurora-B. Cell Cycle 8, 2984-2994 (2009).
38. Szafran, A.T.,
Hartig, S., Sun, H., Uray, I.P., Szwarc, M., Shen, Y., Mediwala, S.N., Bell,
J., McPhaul, M.J., Mancini, M.A. & Marcelli, M. Androgen receptor mutations
associated with androgen insensitivity syndrome: a high content analysis
approach leading to personalized medicine. PloS one 4, e8179 (2009).
39. Willems, E.,
Bushway, P.J. & Mercola, M. Natural and synthetic regulators of embryonic
stem cell cardiogenesis. Pediatr Cardiol 30, 635-642 (2009).
40. Berno, V.,
Amazit, L., Hinojos, C., Zhong, J., Mancini, M. G., Sharp, Z. D., Mancini, M.
A. Activation of estrogen receptor-alpha by E2 or EGF induces temporally
distinct patterns of large-scale chromatin modification and mRNA transcription.
PloS one 3, e2286 (2008).
41. Bushway, P.J.,
Mercola, M. & Price, J.H. A comparative analysis of standard microtiter
plate reading versus imaging in cellular assays. Assay and drug development
technologies 6, 557-567 (2008).
42. Szafran, A.T.,
Szwarc, M., Marcelli, M. & Mancini, M.A. Androgen receptor functional
analyses by high throughput imaging: determination of ligand, cell cycle, and
mutation-specific effects. PloS one 3, e3605 (2008).
43. Amazit, L.,
Pasini, L., Szafran, A.T., Berno, V., Wu, R.C., Mielke, M., Jones, E.D.,
Mancini, M.G., Hinojos, C.A., O'Malley, B.W. & Mancini, M.A. Regulation of
SRC-3 intercompartmental dynamics by estrogen receptor and phosphorylation.
Molecular and cellular biology 27, 6913-6932 (2007).
44. Garcia Osuna,
E., Hua, J., Bateman, N.W., Zhao, T., Berget, P.B. & Murphy, R.F.
Large-scale automated analysis of location patterns in randomly tagged 3T3
cells. Ann Biomed Eng 35, 1081-1087 (2007).
45. Huang, Y., Qiu,
J., Dong, S., Redell, M.S., Poli, V., Mancini, M.A. & Tweardy, D.J. Stat3
isoforms, alpha and beta, demonstrate distinct intracellular dynamics with prolonged
nuclear retention of Stat3beta mapping to its unique C-terminal end. The
Journal of biological chemistry 282, 34958-34967 (2007).
46. Prigozhina,
N.L., Zhong, L., Hunter, E.A., Mikic, I., Callaway, S., Roop, D.R., Mancini,
M.A., Zacharias, D.A., Price, J.H. & McDonough, P.M. Plasma membrane assays
and three-compartment image cytometry for high content screening. Assay and
drug development technologies 5, 29-48 (2007).
47. Berno, V.,
Hinojos, C.A., Amazit, L., Szafran, A.T. & Mancini, M.A. High-resolution, high-throughput
microscopy analyses of nuclear receptor and coregulator function. Methods
Enzymol 414, 188-210 (2006).
48. Cho, C.Y., Koo,
S.H., Wang, Y., Callaway, S., Hedrick, S., Mak, P.A., Orth, A.P., Peters, E.C.,
Saez, E., Montminy, M., Schultz, P.G. & Chanda, S.K. Identification of the
tyrosine phosphatase PTP-MEG2 as an antagonist of hepatic insulin signaling.
Cell Metab 3, 367-378 (2006).
49. Marcelli, M.,
Stenoien, D.L., Szafran, A.T., Simeoni, S., Agoulnik, I.U., Weigel, N.L.,
Moran, T., Mikic, I., Price, J.H. & Mancini, M.A. Quantifying effects of
ligands on androgen receptor nuclear translocation, intranuclear dynamics, and
solubility. J Cell Biochem 98, 770-788 (2006).
50. Mikic, I.,
Planey, S., Zhang, J., Ceballos, C., Seron, T., von Massenbach, B., Watson, R.,
Callaway, S., McDonough, P.M., Price, J.H., Hunter, E. & Zacharias, D. A
live cell, image-based approach to understanding the enzymology and
pharmacology of 2-bromopalmitate and palmitoylation. Methods Enzymol 414,
150-187 (2006).
51. Mukherji, M.,
Bell, R., Supekova, L., Wang, Y., Orth, A.P., Batalov, S., Miraglia, L.,
Huesken, D., Lange, J., Martin, C., Sahasrabudhe, S., Reinhardt, M., Natt, F.,
Hall, J., Mickanin, C., Labow, M., Chanda, S.K., Cho, C.Y. & Schultz, P.G.
Genome-wide functional analysis of human cell-cycle regulators. Proceedings of
the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 103,
14819-14824 (2006).
52. Prigozhina, N.L.
& Waterman-Storer, C.M. Decreased polarity and increased random motility in
PtK1 epithelial cells correlate with inhibition of endosomal recycling. J Cell
Sci 119, 3571-3582 (2006).
53. Sharp, Z.D.,
Mancini, M.G., Hinojos, C.A., Dai, F., Berno, V., Szafran, A.T., Smith, K.P.,
Lele, T.P., Ingber, D.E. & Mancini, M.A. Estrogen-receptor-alpha exchange
and chromatin dynamics are ligand- and domain-dependent. J Cell Sci 119,
4101-4116 (2006).
54. Shen, F.,
Hodgson, L., Rabinovich, A., Pertz, O., Hahn, K. & Price, J.H. Functional
proteometrics for cell migration. Cytometry. Part A : the journal of the
International Society for Analytical Cytology 69, 563-572 (2006).
55. Shen, F. &
Price, J.H. Toward complete laser ablation of melanoma contaminant cells in a
co-culture outgrowth model via image cytometry. Cytometry. Part A : the journal
of the International Society for Analytical Cytology 69, 573-581 (2006).
56. Wilson, C.J.,
Si, Y., Thompsons, C.M., Smellie, A., Ashwell, M.A., Liu, J.F., Ye, P.,
Yohannes, D. & Ng, S.C. Identification of a small molecule that induces
mitotic arrest using a simplified high-content screening assay and data
analysis method. Journal of biomolecular screening 11, 21-28 (2006).
57. Harada, J.N.,
Bower, K.E., Orth, A.P., Callaway, S., Nelson, C.G., Laris, C., Hogenesch,
J.B., Vogt, P.K. & Chanda, S.K. Identification of novel mammalian growth
regulatory factors by genome-scale quantitative image analysis. Genome Res 15,
1136-1144 (2005).
58. Morelock, M.M.,
Hunter, E.A., Moran, T.J., Heynen, S., Laris, C., Thieleking, M., Akong, M.,
Mikic, I., Callaway, S., DeLeon, R.P., Goodacre, A., Zacharias, D. & Price,
J.H. Statistics of assay validation in high throughput cell imaging of nuclear
factor kappaB nuclear translocation. Assay and drug development technologies 3,
483-499 (2005).
59. Price, J.H.,
Goodacre, A., Hahn, K., Hodgson, L., Hunter, E.A., Krajewski, S., Murphy, R.F.,
Rabinovich, A., Reed, J.C. & Heynen, S. Advances in molecular labeling,
high throughput imaging and machine intelligence portend powerful functional
cellular biochemistry tools. J Cell Biochem Suppl 39, 194-210 (2002).
60. Bajaj, S.,
Welsh, J.B., Leif, R.C. & Price, J.H. Ultra-rare-event detection
performance of a custom scanning cytometer on a model preparation of fetal
nRBCs. Cytometry 39, 285-294 (2000).
III. CyteSeer Software Platform
61. Chung, C.H.,
Miller, A., Panopoulos, A., Hao, E., Margolis, R., Terskikh, A. & Levine,
F. Maternal embryonic leucine zipper kinase regulates pancreatic ductal, but
not beta-cell, regeneration. Physiological reports 2(2014).
62. Bhavane, R.,
Badea, C., Ghaghada, K.B., Clark, D., Vela, D., Moturu, A., Annapragada, A.,
Johnson, G.A., Willerson, J.T. & Annapragada, A. Dual-energy computed
tomography imaging of atherosclerotic plaques in a mouse model using a
liposomal-iodine nanoparticle contrast agent. Circulation. Cardiovascular
imaging 6, 285-294 (2013).
63. Mediwala, S.N.,
Sun, H., Szafran, A.T., Hartig, S.M., Sonpavde, G., Hayes, T.G., Thiagarajan,
P., Mancini, M.A. & Marcelli, M. The activity of the androgen receptor
variant AR-V7 is regulated by FOXO1 in a PTEN-PI3K-AKT-dependent way. The
Prostate 73, 267-277 (2013).
64. Zhang, Y.,
Davis, C., Sakellariou, G.K., Shi, Y., Kayani, A.C., Pulliam, D., Bhattacharya,
A., Richardson, A., Jackson, M.J., McArdle, A., Brooks, S.V. & Van Remmen,
H. CuZnSOD gene deletion targeted to skeletal muscle leads to loss of
contractile force but does not cause muscle atrophy in ***** mice. FASEB
journal : official publication of the Federation of American Societies for
Experimental Biology 27, 3536-3548 (2013).
65. Colas, A.R.,
McKeithan, W.L., Cunningham, T.J., Bushway, P.J., Garmire, L.X., Duester, G.,
Subramaniam, S. & Mercola, M. Whole-genome microRNA screening identifies
let-7 and mir-18 as regulators of germ layer formation during early
embryogenesis. Genes & development 26, 2567-2579 (2012).
66. Tanifum, E.A.,
Dasgupta, I., Srivastava, M., Bhavane, R.C., Sun, L., Berridge, J.,
Pourgarzham, H., Kamath, R., Espinosa, G., Cook, S.C., Eriksen, J.L. &
Annapragada, A. Intravenous delivery of targeted liposomes to amyloid-beta
pathology in APP/PSEN1 transgenic mice. PloS one 7, e48515 (2012).
67. Willems, E.,
Cabral-Teixeira, J., Schade, D., Cai, W., Reeves, P., Bushway, P.J., Lanier,
M., Walsh, C., Kirchhausen, T., Izpisua Belmonte, J.C., Cashman, J. &
Mercola, M. Small molecule-mediated TGF-beta type II receptor degradation
promotes cardiomyogenesis in embryonic stem cells. Cell stem cell 11, 242-252
(2012).
68. Larkin, L.M.,
Davis, C.S., Sims-Robinson, C., Kostrominova, T.Y., Van Remmen, H., Richardson,
A., Feldman, E.L. & Brooks, S.V. Skeletal muscle weakness due to deficiency
of CuZn-superoxide dismutase is associated with loss of functional innervation.
American journal of physiology. Regulatory, integrative and comparative
physiology 301, R1400-1407 (2011).
69. Willems, E.,
Spiering, S., Davidovics, H., Lanier, M., Xia, Z., Dawson, M., Cashman, J.
& Mercola, M. Small-molecule inhibitors of the Wnt pathway potently promote
cardiomyocytes from human embryonic stem cell-derived mesoderm. Circulation
research 109, 360-364 (2011).
70. Sun, S.,
Sprenger, C.C., Vessella, R.L., Haugk, K., Soriano, K., Mostaghel, E.A., Page,
S.T., Coleman, I.M., Nguyen, H.M., Sun, H., Nelson, P.S. & Plymate, S.R.
Castration resistance in human prostate cancer is conferred by a frequently
occurring androgen receptor splice variant. The Journal of clinical
investigation 120, 2715-2730 (2010).
71. McKeithan, W.L., Colas, A.R., Bushway, P.J., Ray, S.
& Mercola, M. Serum-Free Generation of Multipotent Mesoderm (Kdr+)
Progenitor Cells in Mouse Embryonic Stem Cells for Functional Genomics
Screening. in Current Protocols in Stem Cell Biology (John Wiley & Sons,
Inc., 2007).
|